In this post, I will tell you about cybersecurity tips and necessary measures to take when data leak. cybersecurity is a necessity. From online banking and shopping to social media and remote work, our lives are increasingly connected, making our personal data vulnerable to cyber threats. With cybercrime expected to cost the world over $12 trillion annually by 2025, it’s crucial to adopt proactive online safety measures.
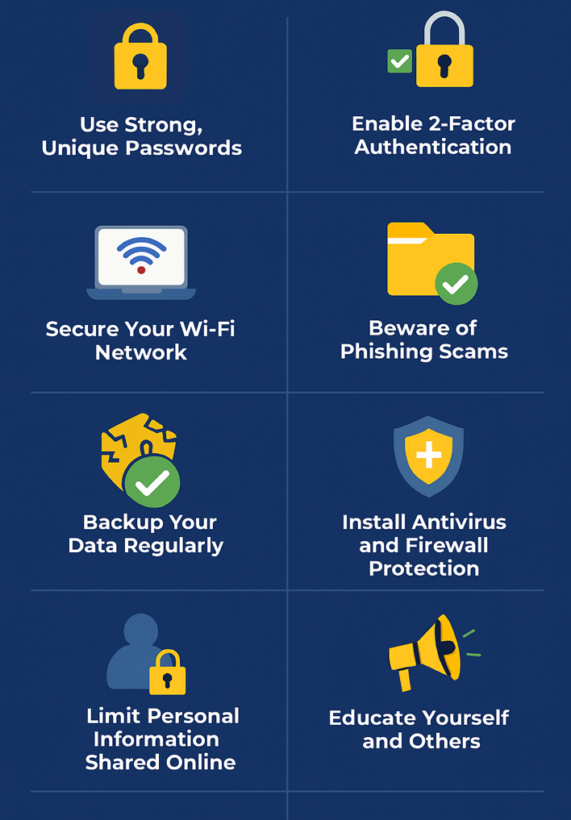
10 Cyber Security Tips To Keep Your Data Safe
- Use Strong, Unique Passwords
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
- Keep Software and Devices Updated
- Beware of Phishing Scams
- Secure Your Wi-Fi Network
- Backup Your Data Regularly
- Limit Personal Information Shared Online
- Install Antivirus and Firewall Protection
- Use Secure Websites Only
- Educate Yourself and Others
1. Use Strong, Unique Passwords
Securing your devices and online accounts with passwords is one of the most effective ways to keep your data safe. Since hackers possess some of the most advanced software that makes it easy for them to break passwords within seconds, you require a mix that will surely conceal your information. The strongest password should have a minimum of 8 characters with a combination of both uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, as well as special characters. Protect each of your accounts by using a brand new combination so don’t repeat the passwords, particularly for weak or work-related accounts. Don’t use words that would easily be associated with you like your kids’ names, birthdays, or the location of your primary school. Although it might be a good choice to use your wedding date and your wife’s maiden name as strong, hackers are able to obtain such information from all sorts of places (such as social media) and access your accounts. Instead, make sure the combination is random and does not have any meaning, like “Ofh61D3x!?”
Since such combinations are much more complex and hard to recall, most employees jot them down in notebooks or on sheets of paper they leave in open view on the workplace. It’s another error that can possibly breach the security of your account since anyone passing by your desk can access your login information. Password managers securely save and keep all your passcodes so you don’t have to. They can even generate the strongest combinations for you!
Software such as LastPass, RememBear, NordPass, or Sticky Passwords are absolutely free to download and use, so you won’t have to pay a cent to keep yourself safe at work.
Alternatively, you can provide even greater security to your accounts through the use of passphrases rather than one-word passwords. These typically consist of a single sentence or a phrase that you yourself have determined. Their lengths being unusual, it becomes a significantly tougher challenge for cybercrooks to crack even with the most sophisticated hacking tools. 2FA asks you to enter two different verification processes when you access your accounts. The first authentication step is nearly always by entering a proper password, and the second one varies based on the platform you are accessing. You’ll be asked very frequently to enter a different email address or a phone number upon which the site will send you a random access code or link. You can only log in to your account by entering the proper combination or by clicking on the link.
2. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Most sites now enable you to use this double protection on your profiles — you can even turn it on to restrict unauthorized use of your iPhone. The process of setting it up is incredibly easy, and you will be able to activate the two-factor authentication in your account settings on most websites. If you cannot find it, you can always call customer support or your IT department and they will do it for you.
Hackers make highly generic messages using scare methods to get you to open a link or download an attached document. As soon as you are made to respond to a request of this nature, you open up scammers to easy access of your computer and the information contained in it by downloading malware that gains access to the network immediately. It’s estimated at over 3.4 billion phishing emails dispatched daily. You must take a keen eye for detail since scammers go an extra mile to cover up anything which may appear suspicious. Be cautious of spelling errors, click-bait links which may have too good to be true appearance, strange requests, and strange spellings, especially in the email address. Don’t be in a hurry, double-check every letter in the email address, and if possible, check it with the company’s email address shown on their website. You can also make a call to the organization in question to confirm whether they attempted to contact you recently. Lastly, you should also forward the email to your IT department so that they can perform further checks.
3. Beware of Phishing Scams
Phishing is one of the most popular scamming methods used to steal your vulnerable information or gather a company’s data. Engage with the email received only if you are given the green light by the experts and 100% certain the sender is genuine. Be aware that phishing emails don’t always mimic third-party companies — many of them seem like they’re sent from your colleagues, employers, or even friends. This makes them a lot more believable, as you’re less likely to be suspicious of the contents of the received email. To avoid compromising your and your company’s data, always confirm the sender’s identity using another method of communication. You can easily and swiftly authenticate the source of such an email by reaching out to or messaging the supposed sender via an online platform your business employs, like Slack or others. Alternatively, you can query them directly if the supposed sender is in the same department or building as you.
4. Secure Your Wifi Network
As more business organizations are adopting Cloud storage, employees can do their work from home or a public area, such as a library or cafe. Still, working remotely denies you any cyber protection used in your workplace and exposes you to being an easier target for cyberattackers. You should never perform any work-related task using an unsecured WiFi network in hotels, restaurants, cafes, libraries, and other public spaces where anyone can use it. Public networks can be easily intercepted by active or idle hackers, and they can crack into every device which is on it. Then they infect their victims with malware, such as worms and viruses, or conduct a Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attack which enables them to intercept and gain access to all information transmitted between you and the internet.
If your job entails doing your work when you’re outside the office (for instance on a business trip) consider securing your devices with a VPN. A VPN connection will automatically secure your web traffic providing you with complete anonymity even when you are on public WiFi networks. Encryption of data prevents hackers from intercepting what you send and receive and keeps you safe from malicious users ready to hack your devices. By establishing a link with a VPN server before accessing any public hotspot, you’ll be invisible to prying eyes no matter where you get your work done.
5. Backup Your Data Regularly
Backing up existing files doesn’t protect you against cyber attacks, but it can save you a headache in case your device gets stolen, lost, or compromised in an attack. That’s because you’ll be able to recover the most recent version of your files by downloading their backup from the cloud and installing them on another device.
There are two very different types of backups: a full backup and incremental backup. The first one works by duplicating all of your company’s assets, such as files, databases, and systems, and saving them on another device or on the cloud. An incremental backup supplements the full backup by duplicating any files you have created or changed since the last full backup. Experts advise that both types should be done routinely since it’ll guarantee you’ll always have access to the latest version of your company’s data.
Though it is not always practical to manually back up your data on a daily basis since it will consume too much time, find out if the system will permit automatic backup weekly or monthly. These can also be instructed to store directly in the company’s cloud account or an independent device, such as a USB flash drive or hard drive memory. Which one you use is your choice and your company, but consider the advantages and disadvantages of each before you decide.
Storing your backups on an external device will increase the responsibility to protect that device. You want to keep it in a safe location where no one can steal it or alter it. Conversely, although storing backups in the cloud is the simplest means of maintaining and restoring data from any location, the online technology is still very insecure. Since the cloud is still a relatively new technology, it has several vulnerabilities that can easily be exploited by hackers without the knowledge of cyber security professionals. This can result in potentially giving all of your business’s information to an attacker if your cloud account is breached.
6. Limit Personal Information Shared Online
When discussing cyber security threats, most guides speak primarily of hackers attempting to gain entry from the exterior, but that is not always true. It’s actually quite prevalent for the cyber attacks to be from within with statistics demonstrating that 30% of hacking attacks are now being perpetrated by existing or former employees. Insider threat defines a situation where an individual is acting in a bad way with forethought — but it can also refer to numerous accidents that occur due to human error or carelessness. Whatever their cause, insider threats expose your information to potential leaks and redistribution into the wrong hands.
That is why it is crucial that you do not expose yourself to those you work with by restricting sensitive information visible on your desk or workspace. Make sure you place any folders carrying sensitive information either concerning company procedures or your own data away. Conceal any USBs and, whenever possible, lock your devices in a safety cabinet or a locker. Refrain from writing down your passwords and login credentials in notebooks or scraps of paper, especially if you’d leave them in the open.
Access should be limited for every employee to only those parts of the company network they need. Unless you’re compelled to share particular accounts and reports with your colleagues, you should never share your login information with anyone. That will reduce potential inside dangers and hinder those who bide their time to strike with sinister intent.
It’s also advisable to turn off or log out of your work equipment every time you’re about to leave it unattended, even when it’s just for a trip to the toilet. This will be a very effective way to keep people from digging through your files without your consent. It might be hard to remember to lock your computer each time you leave it, but it’s a habit you should try to cultivate. Most programs these days have the feature to automatically shut down after a specified duration of inactivity. Your IT department can assist you in setting it up, so you better not ask!
7. Install Antivirus and Firewall Protection
Installing antivirus software and a firewall is a foundational cybersecurity measure for both individuals and organizations. Antivirus software scans, blocks, and deletes malicious code like viruses, worms, trojans, ransomware, and spyware from invading your system. Antivirus software operates in real time and scans files, downloads, and web traffic continuously for threats. A firewall, however, provides a virtual shield between your computer and the internet, keeping a watchful eye on incoming and outgoing traffic. It prevents unknown access and helps maintain data integrity or intrusions. While antivirus defends against Trojan horses, firewalls target network attacks—so the two are complementary. Make sure your security software comes from a reputable vendor and is updated to guard against the newest attacks. Without these safeguards, your system is open to attack, which can result in loss of data, identity theft, and system compromise.
8. Use Secure Websites Only
Using secure websites is essential for maintaining online safety and protecting sensitive data such as passwords, credit card numbers, and personal details. Always check that a site uses HTTPS rather than just HTTP—this “S” stands for secure and means the site uses encryption to protect data exchanged between your browser and the server. Most browsers display a padlock icon in the address bar to indicate a secure connection. Avoid entering personal information on websites that lack this encryption, especially during financial transactions or account logins.
9. Take Precautions to Protect Yourself
With more than 20 well-known cyber attacks, your information requires your protection more than ever before — particularly at the workplace. Since your employer keeps your personal information, including your social security numbers, banking information, and home address, you shouldn’t just depend on its cyber protection alone. Rather, take yourself out of the potential hacking target zone by ensuring you abide by at least a few of the cyber security guidelines discussed above.
Besides establishing a cyber security regimen, bear in mind that cyber attackers continuously evolve and enhance their methods to evade even the most stringent security measures. You must keep ahead of it by being familiar with all security policies instituted in your workplace along with the newest cyber security practices.
10. Educate Yourself and Others
Cybersecurity is a shared responsibility, and education is one of the most effective ways to strengthen digital safety. Knowing current threats like phishing, malware, and social engineering helps you to notice and steer clear of them. Because technology is changing all the time, cybercrooks are continually finding new ways to take advantage of users, so continuing to educate yourself is necessary. Join webinars, read good cybersecurity blogs, or take introductory online courses. Equally crucial is spreading awareness: educate colleagues, buddies, or loved ones on how to generate strong passwords, identify suspicious links, and protect their data safely. In the workplace, cybersecurity training can largely eliminate human error, the leading cause of security incidents. By instilling a culture of cyber awareness, everyone becomes a line of defense. Remember: your know-how might save someone else from becoming a victim.